The NHSmail team frequently review the security posture and security level of the platform. One threat vector identified has been compromised accounts. Accounts of this nature are a big threat to any organisation.
To protect the NHSmail platform, administrators are now able to mark an account as compromised, triggering a corresponding workflow to ensure the account is locked down. The process will include account disablement, a password reset and the enablement of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on the account. In addition, any mailbox rules on the account will be disabled due to the account being marked as compromised; once the account has been remediated, it is the user’s responsibility to validate any mailbox rules which are needed and re-enable them.
For security reasons, enablement of MFA is crucial. It increases protection for users by making it more difficult for someone else to sign in to their NHSmail account. It requires the user to provide two different forms of identity: user password and a contact method. When MFA is enabled, accounts are added to the MFA Conditional Access Standard policy.
Compromised Account
A compromised account can typically be associated with behaviour that is deemed ‘not normal’. This may be related to one or more of the following examples:
- A sudden increase in emails being sent
- The content within an email sent being inappropriate or malicious
- Account login activity occurring within unsociable timescales and showing a clear change from previous activity
To ensure the NHSmail platform and its users are protected from malicious activity where possible, administrators should mark an account as compromised in any case where they perceive an account to be behaving abnormally. Additionally, an account can be marked as compromised as many times as administrators see fit.
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) provides an additional layer of security to your NHSmail account when signing in to NHSmail via a web browser. It achieves this by requiring you to provide two different forms of identity on sign-in: your NHSmail password and a contact method.
MFA will automatically be enabled if your account is marked as compromised. For security reasons, once it has been enabled in this way, it can never be permanently disabled. This means that MFA will remain enabled on your account, regardless of whether the account is remediated or not.
Once your account has been remediated, you will regain the ability to sign in to NHSmail with your username and new password. In addition to this, you will be required to authenticate your sign-on via a secondary method (for example, a security code will be sent to your mobile phone). This two-step verification will help keep your NHSmail account secure.
To find out the MFA status of users within your organisation, administrators can download the MFA Status Report from the ‘Admin Reports’. More information about the Admin Reports can be found here.
For further information relating to setting up MFA on your devices, please refer to: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – NHSmail Support
How to Mark an account as Compromised
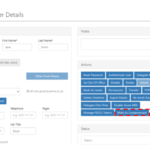 1. After identifying a potentially compromised account, on the relevant ‘Users Details’ page, click on the ‘Mark as Compromised’ button
1. After identifying a potentially compromised account, on the relevant ‘Users Details’ page, click on the ‘Mark as Compromised’ button
 2. Once the dialog box has appeared, select ‘Confirm’ to proceed. If you do not wish for the account to be marked as compromised, select ‘Cancel’. This will close the dialog box and the user account will remain unchanged.
2. Once the dialog box has appeared, select ‘Confirm’ to proceed. If you do not wish for the account to be marked as compromised, select ‘Cancel’. This will close the dialog box and the user account will remain unchanged.
3. After selecting ‘Confirm’ on the dialog box, you will be directed to the User Management page and notified whether the account has been successfully marked as compromised.
Compromised Account View
A compromised account can be identified from the following updates to the User Details page:
- Addition of the following note within the Notes field:
“Account has been identified as compromised. If you are updating this account, please proceed with caution. DD-MM-YYYY.”
Note: DD-MM-YYYY will reflect the date the account was marked as compromised.
- Status will be set to “Disabled”
While an account is compromised, as an administrator, you will be restricted in your ability to update the account. You will only be able to trigger the following actions:
- Deletion of the account
- Deletion of the user’s OneDrive
- Delegation of the user’s OneDrive
- Ability to export the user’s details
- Remediation of the compromised account
The “Reset Password”, “Delegate Mailbox” and “Set Out Of Office” actions will be disabled whilst the account is compromised. To trigger any of these three actions, you will first need to remediate the compromised account.
For added security, once an account is marked as compromised, all user access will be revoked. This includes:
- Disabling the user in Azure AD
- Revoking the user’s Azure AD refresh tokens
- Disabling the user’s Exchange Online mailbox rules. Please note, after remediation users will need to re-enable the rules previously set up, and also assess rules that may not have been set up by themselves in Exchange.
- Disabling the user’s devices
- Removal of the Mobile Phone number as authentication method (MFA) associated with the account. This will require re-setting up again after the account has been remediated.
- Delegate access previously granted needs to be reconfigured as part of remediating the account.
Links
| Last Reviewed Date | 01/08/2024 |