1. Article summary
Copilot Agents are Microsoft’s capability for extending Copilot to interact with custom data sources and systems, enabling tailored, goal-focused solutions within broader business processes. In this article, you will learn:
- What Copilot Agents are
- The different types of Agents available
- Agent patterns and their typical use cases
2. What are Copilot Agents?
Copilot Agents are specialised AI assistants, built to work within the broader Microsoft Copilot framework, that automate and execute specific tasks and business processes using your organisation’s data and AI capabilities. Think of a Copilot as the interactive interface, and Agents as specialised applications that perform actions, such as a Researcher Agent gathering information from your work data and the web, or a Sales Agent qualifying leads, to extend Copilot’s functionality beyond general assistance.
For more information about Copilot Agents and Microsoft’s wider Copilot Extensibility tools, check out Extend Microsoft 365 Copilot | Microsoft Learn.
The following platforms and Agents are now available:
| Platform | Agent Type |
| SharePoint | Declarative Agent |
| Copilot Studio Lite (previously called Agent Builder) | Declarative Agent |
| Copilot Studio Full | Declarative Agent |
| Copilot Studio Full | Custom Engine Agents (without Azure Open AI) |
| M365 Agents Toolkit/Visual Studio Code | Declarative Agents (without Azure Open AI) |
(Custom engine Agents built with Microsoft 365 Agents Toolkit or Azure AI Foundry are out of scope and not generally available. The development of AI Agents built with other frameworks are also out of scope.)
3. Understand Different Types of Agents
Agents
These are specialised assistants focused on specific subjects, powered by organisational knowledge and actions to automate business process.
There are two types of Copilot Agents:
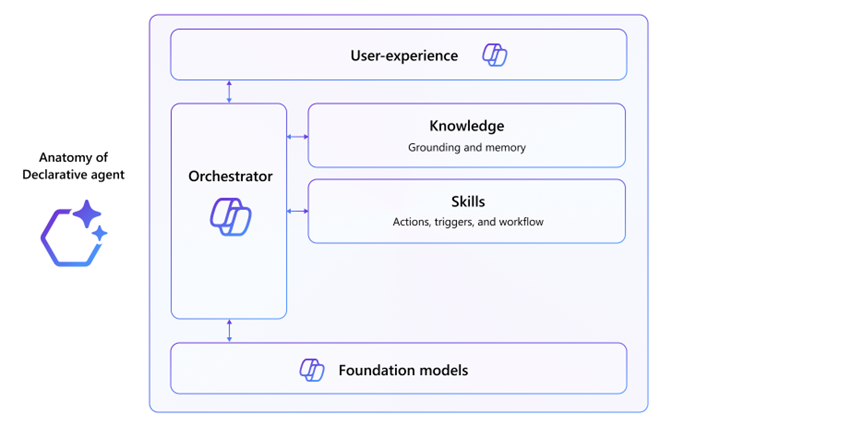
- Declarative Agents leverage the Microsoft 365 Copilot orchestrator and foundation models. They are natively integrated within the Microsoft 365 environment and can utilise Copilot connectors, plugins and actions to enable more advanced capabilities. For more information on Declarative Agents, see Declarative Agents for Microsoft 365 Copilot | Microsoft Learn.
- Custom Engine Agents are fully customised AI assistants useful for scenarios that require complex workflows, orchestration, or specific language models Building a Custom Engine Agent might require additional hosting for models and orchestrators and ensuring compliance with security and responsible AI policies. Copilot Studio provides the capability to select readily available models for use out-the-box. For more information on Custom Engine Agents, check out Custom Engine Agents for Microsoft 365 | Microsoft Learn
 Developer tools for building Copilot Agents
Developer tools for building Copilot Agents
Agent Patterns
Microsoft 365 Copilot and Copilot Agents offer a diverse range of agent types and implementation approaches. While these Agents share overlapping capabilities, each is optimised for specific scenarios, use cases and time to deployment. While these Agent patterns are by no means prescriptive, they may be helpful to refer to when considering what kind of Agent you want to build and discussing your Agent with others.
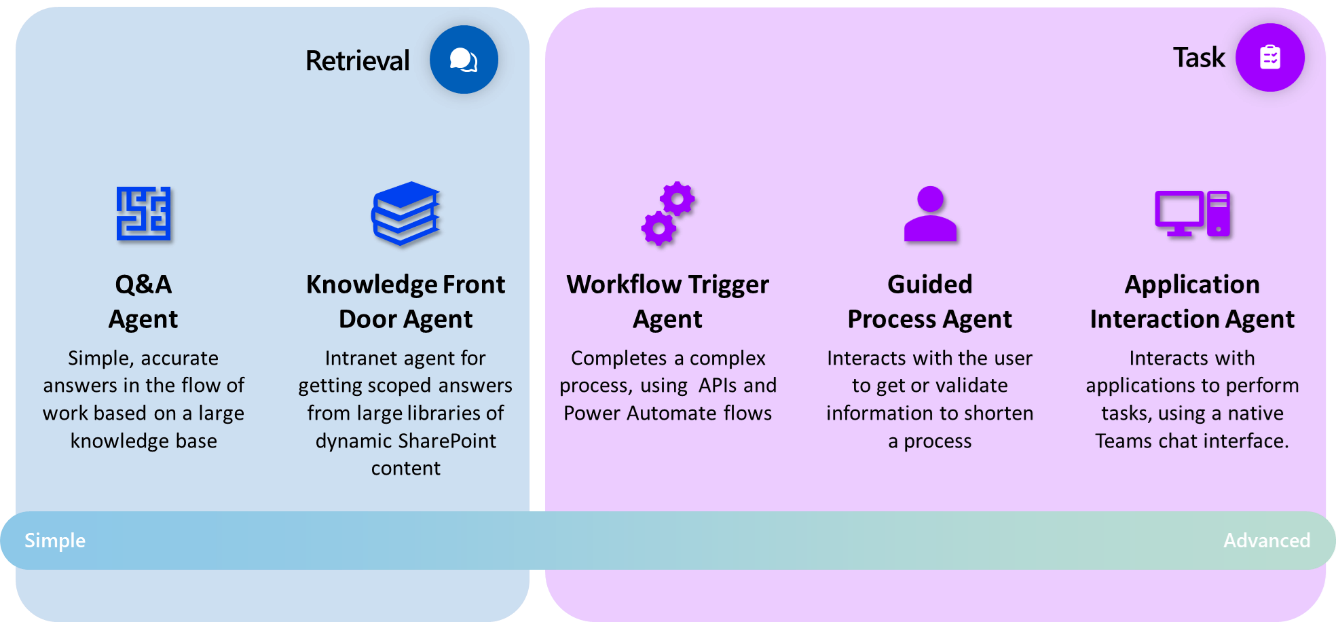
Agents are split into three complexities: Retrieval, Task and Autonomous.
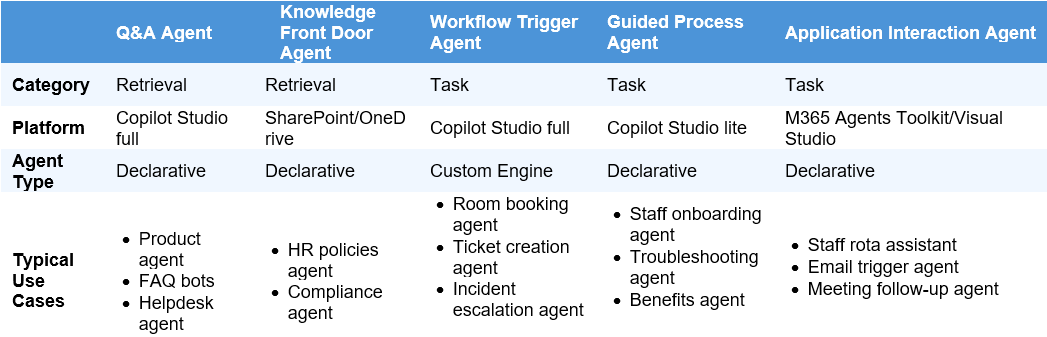
Agent Type: Copilot Studio Full – Declarative Agent
Pattern Description: Supports fast, single question and response for retrieving static information from a predefined knowledge base within Microsoft 365 Copilot entry points for example, Copilot Chat in Teams, Microsoft 365 Copilot on the web. Best suited for scenarios where extensibility can be facilitated through connectors and plugins, and may be used in conjunction with other Agents, through a human orchestration led approach.
Typical Use Cases:
- Product support Agent
- Power platform support Agent
- FAQ bots
- Helpdesk Agent
Agent Type: SharePoint Agent
Pattern Description: Able to answer questions based on knowledge within a scope already identified by the requestor, as part of a SharePoint site or library the Agent will respond from the context of documents in that site. Often used as a ‘front door’ to information. These Agents can either be used in a sidecar experience in SharePoint, or in the flow of work in Microsoft Teams, through chat, channel or meeting interaction.
Typical Use Cases:
- HR policies Agent
- User research Agent
- User-centred design Agent
Agent Type: Copilot Studio Full – Custom Engine Agent
Pattern Description: Trigger backend logic, Power Automate flows, or API calls from user conversations using custom orchestration. Integrate with richer low-code capabilities like topics for more deterministic outcomes where necessary, and pro-dev capabilities for more complex scenarios.
- Typical Use Cases:
- Incident management Agent
- Room booking Agent
Agent Type: Copilot Studio Lite – Declarative Agent
Pattern Description: Facilitates structured, multi-step interactions where user input is collected and validated across a guided flow. These Agents do not provide the capability to extend Microsoft 365 Copilot with maker connected data sources or services. These allow makers to provide Microsoft 365 Copilot with a scoped role or focus for achieving a task.
Typical Use Cases:
- Provide local office and area relevant information
- Conduct research on consumer trends in the healthcare industry
- Content summarisation
Agent Type: M365 Agents Toolkit/Visual Studio Code – Declarative Agent (without Azure Open AI)
Pattern Description: Agent built for Microsoft 365 Copilot (chat) that integrates with internal systems to manage schedules, shifts, or appointments, or other scenarios. Supports secure, authenticated interactions and action taking with API plugins. These agents also enable several data integration capabilities with Microsoft 365 such as using people data or scoping the focus of Copilot to a single mailbox.
Typical Use Cases:
- Staff rota assistant
- Meeting follow-up Agent
- Actions Assistant
4. Find out more
- How to Guide for Agent Building
- Copilot Extensibility FAQs
- Copilot Extensibility Guardrails
- How to Guide for Copilot Extensibility Management
| Last Reviewed Date | 14/10/2025 |